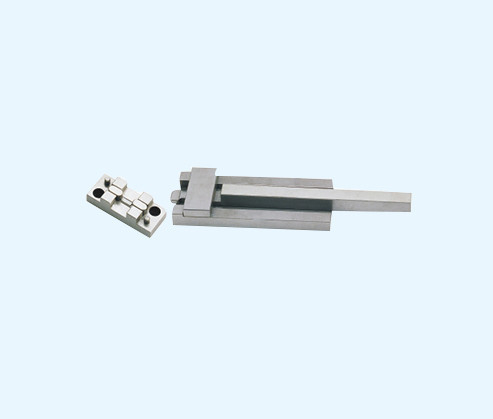
Mold accessories refer to the general term for metal accessories exclusively used in the mold industry for stamping molds, plastic molds, or FA automation equipment. Mold accessories include: punch, punch, guide post, guide sleeve, ejector pin, driver, steel ball sleeve, oil-free guide sleeve, oil-free sliding plate, guide post components, etc.
1. Wear resistance
When the billet undergoes plastic deformation in the mold cavity, it flows and slides along the surface of the cavity, causing severe friction between the cavity surface and the billet, resulting in the failure of the mold due to wear. So the wear resistance of materials is one of the most basic and important properties of molds.
Hardness is the main factor affecting wear resistance. In general, the higher the hardness of mold parts, the smaller the wear amount, and the better the wear resistance. In addition, wear resistance is also related to the type, quantity, morphology, size, and distribution of carbides in the material.
2. Strong resilience
The working conditions of molds are mostly very harsh, and some often bear large impact loads, leading to brittle fracture. To prevent sudden brittle fracture of mold parts during operation, the mold should have high strength and toughness. The toughness of molds mainly depends on the carbon content, grain size, and microstructure of the material.
3. Fatigue fracture performance
During the working process of molds, long-term cyclic stress often leads to fatigue fracture. Its forms include low-energy multiple impact fatigue fracture, tensile fatigue fracture, contact fatigue fracture, and bending fatigue fracture. The fatigue fracture performance of molds mainly depends on their strength, toughness, hardness, and the content of inclusions in the material.
4. High temperature performance
When the working temperature of the mold is high, it will cause a decrease in hardness and strength, leading to early wear or plastic deformation of the mold and failure. Therefore, the mold material should have high resistance to tempering stability to ensure that the mold has high hardness and strength at working temperature.
5. Cold and hot fatigue resistance performance
Some molds are in a state of repeated heating and cooling during the working process, causing the surface of the mold cavity to be subjected to tensile and compressive stress, resulting in surface cracking and peeling, increasing friction, hindering plastic deformation, reducing dimensional accuracy, and leading to mold failure. Cold and hot fatigue is one of the main forms of failure in hot work molds, and such molds should have high resistance to cold and hot fatigue.
6. Corrosion resistance
Some molds, such as plastic molds, may decompose and release highly corrosive gases such as HCI and HF due to the presence of chlorine, fluorine, and other elements in the plastic during operation. These gases can corrode the surface of the mold cavity, increase its surface roughness, and exacerbate wear and failure.




 +86 13790680950
+86 13790680950

 Leaving a message.
Leaving a message. 