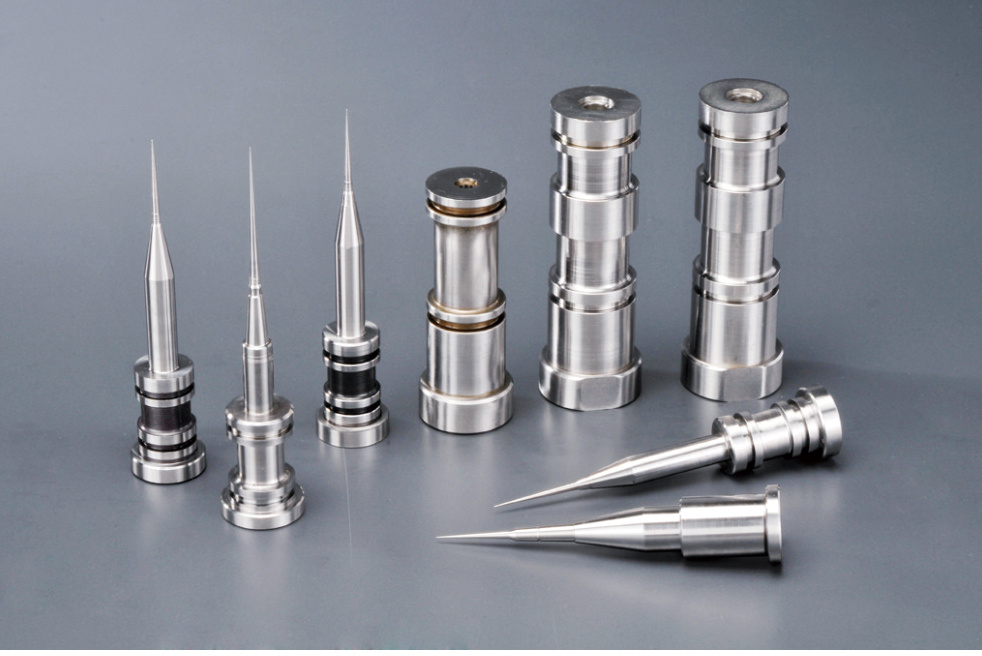
Process control of precision machining of molds
The overall guiding principle for the processing of mold parts is to adaptively process different mold parts, materials, shapes, and technical requirements, with many optional solutions. However, achieving the best processing effect and economy through controlling the processing process is our focus. According to the appearance and shape of mold parts, they can be mainly divided into three categories: shafts, disks, plates, and molded heterogeneous parts. The general process for these three types of parts is rough machining, semi precision machining (quenching, tempering), precision grinding, electrical machining, fitter trimming, and assembly machining.
1. Heat treatment of mold parts
2. Grinding and processing of mold parts
3. Electrical machining of mold parts
4. Surface treatment of mold parts
The content of surface treatment for forming includes the absence of pores on the steel surface, uniform hardness, small differences in anisotropic characteristics, low inclusions, and stress concentration areas such as tool marks and wear marks left on the surface of the part during processing. Therefore, after the processing is completed, it is necessary to strengthen the surface of the parts by mechanical polishing, fitter polishing, and polishing to eliminate processing hazards. Blunt the useless edges, sharp angles, and holes of the workpiece. Generally, the surface of electrical machining will have a metamorphic hardening layer of about 6-10 μ m, which is gray white in color. This layer is brittle and has residual stress. Before use, the hardening layer should be fully eliminated by surface polishing and grinding to remove it. To achieve high-quality polishing results, sufficient consideration should be given to the material, shape, hardness, and surface quality of the workpiece during cutting. It is necessary to have high-quality polishing tools, high-quality polishing materials, correct polishing processes, rigorous personnel quality, and a good cleaning environment.
5. Assembly of mold components
In the process of grinding and electrical machining, the workpiece will have a certain degree of magnetization and weak magnetic force, which is easy to adsorb some small impurities. Therefore, before assembly, the workpiece should be fully demagnetized and the surface should be cleaned with ethyl acetate. During the assembly process: (1) first understand and comprehend the assembly diagram, and complete all kinds of parts; (2) List the assembly sequence between each component; (3) Check the dimensional accuracy of each component and clarify the requirements for coordination; (4) Prepare all the necessary tools and then proceed to assemble the mold; (5) First, assemble the guide column guide sleeve and cavity forming block components of the mold frame; (6) Combine the assembly template with the convex and concave molds, and adjust the position of each plate slightly; (7) Open and close the mold, check if the mold action is reliable.
Numerous practices have proven that mold companies focus on controlling the precision machining process of mold parts, which is the long-term and effective way for mold companies to survive and develop. Through process control, it is possible to minimize the occurrence of parts exceeding tolerances and scrap, thereby effectively improving the lifespan of molds in production and stabilizing product quality, which has profound significance.




 +86 13790680950
+86 13790680950

 Leaving a message.
Leaving a message. 